Which Term Describes Immature Red Blood Cells
They are also referred to as immature red blood cells in some circles. Reticulocytes are red blood cells that are still developing.

Peripheral Blood Smear Showing Fragmented Red Blood Cells Rbcs Download Scientific Diagram
What term is used to describe a red blood cell RBC count that is above normal values.
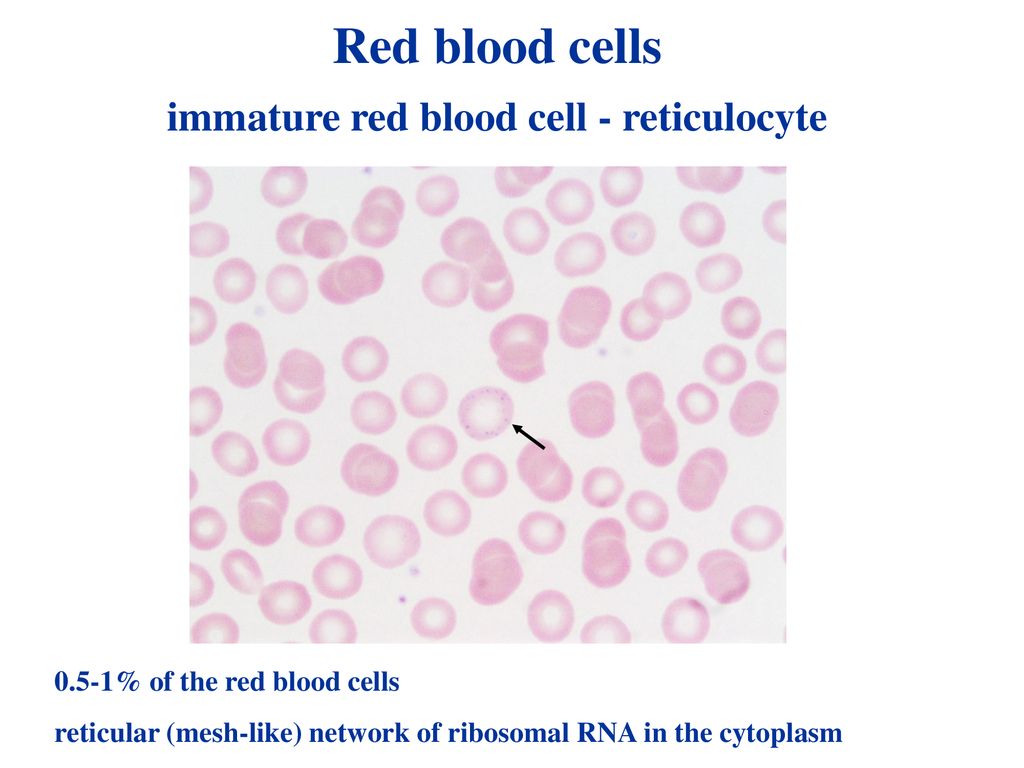
. During the first day or two that it is in the circulation an immature erythrocyte known as a reticulocyte will still typically contain remnants of organelles. Secondly they lose some organelles and their nucleus as they mature into reticulocytes which can be thought of as immature red blood cells. An increase or decrease in reticulocyte count can be an indicator of erythropoiesis activity or failure especially relative to anemias and bone marrow dysfunction1.
And abnormal cells seen on her peripheral blood smear. These red blood cells move oxygen from your lungs to every cell in your body. Immature blood cells are also called blasts.
They are also known as immature red blood cells. Reticulocytes are produced in the bone marrow and then released into the circulation to fight infection. Some of these are released into the peripheral circulation.
Which of the following types of white blood cells fights bacterial infection. Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells RBCs produced in the bone marrow and released into the peripheral blood where they mature into RBCs within 1 to 2 days. What is the typical lifespan of a red blood cell.
In the process of erythropoiesis reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into mature red blood cells. The cell in Image BCI-01 is a nucleated red blood cell RBC. How immature cells grow up to be red blood cells.
Some blasts stay in the marrow to mature. Although nucleated RBCs do not normally appear in the peripheral blood of an adult it is not unexpected in this patients condition owing to hematopoietic bone marrow stress. The cell in this.
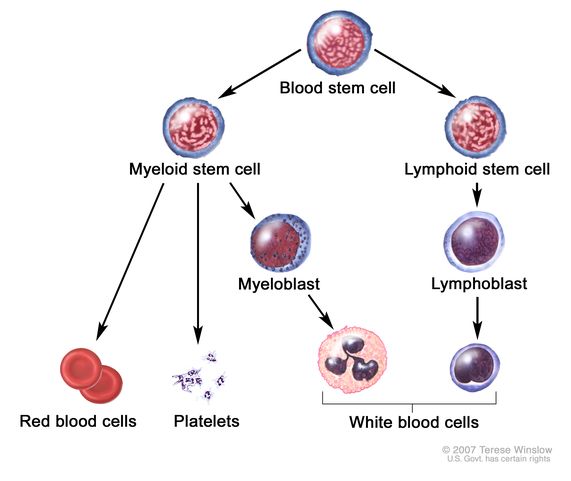
These include red blood cells white blood cells and platelets. Myeloid cells are immature cells that normally become mature red blood cells white blood cells or platelets. The presence of condensed nuclear chromatin in a degenerating cell.
Red blood cells start as immature cells in the bone marrow and after approximately seven days of maturation are released into the bloodstream. These normally survive for around 120. The most common cause of this condition is a deficiency of folic acid and vitamin B12.
What type of white blood cell fights bacterial infection. The clumping or agglutination of an individuals cells by that individuals own serum usually because of the presence of autoantibodies. Its caused by a defective form of hemoglobin that forces red blood cells to assume an abnormal crescent sickle shape.
What term describes the immature neutrophil. Small dots of RNA in a reticulocyte stain eg. These factors place you at increased risk of anemia.
These irregular blood cells die prematurely resulting in a chronic shortage of red blood cells. It is large and red. Megaloblastic macrocytic anemia.
Reticulocytes are made in the bone marrow and sent into the bloodstream. About two days after they form they develop into mature red blood cells. As an erythrocyte matures in the red bone marrow it extrudes its nucleus and most of its other organelles.
This inherited and sometimes serious condition is a hemolytic anemia. Term used to identify immature RBC with small amounts of RNA that precipitate as small punctate dots chunks when the blood is incubated with an intravital dye such as new methylene blue. What term describes a mature red blood cell that contains iron granules or deposits.
What percentage of normal circulating white blood cells are immature and nonsegmented. Reset Help thrombopoletin stimulates cells in the differentiate into red blood cells or Immature red blood cells called are also sometimes released into the blood 3. Old wom-out red blood cells are destroyed by in the The from their hemoglobin is converted to which gives plasma its yellow color erythrocytes epithelal growth factor spleen heme bile smallring bilirubin Glucose oxygen.
Reticulocytes are red blood cells that are still in the process of maturation. Which of the following terms describes red blood cells that are larger than normal. They are called reticulocytes because of a reticular.
Reticulocytes should comprise approximately 12 percent of the erythrocyte count and provide a rough estimate of the rate of. The term acute describes a rapid progression and myeloblastic denotes the origin from myeloid cells. Megaloblastic anemia refers to a condition in which large immature red blood cells are not able to proceed further along their developmental route.
What can be said about the nucleus of the mature circulating red blood cell. What term is used to describe a white blood cell WBC count that is above. The presence of both immature neutrophils and nucleated erythrocytes in the peripheral blood is most accurately called a.
The variation in the size of red blood cells. An arrangement of erythrocytes that appears as a column or stack. Finally reticulocytes lose their remaining organelles as they mature into erythrocytes which are fully mature red blood cells.
What is the upper limit of normal for the fasting blood glucose level. Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells. As the stem cell matures several distinct cells evolve.
Nucleated RBCs are immature erythrocytes that still retain their nucleus. Researchers have identified the mechanism behind red blood cell specialization and revealed that it is controlled by an enzyme called UBE2O. Like mature red blood cells in mammals reticulocytes do not have a cell nucleus.
Unlike many other cells red blood cells have no nucleus and can easily change shape helping them fit through the various blood vessels in. What red blood cell precursor is the last stage to undergo mitosis. What term is used to describe a platelet count below normal.
Acute myeloblastic leukaemia AML is a type of cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells. Others travel to other parts of the body to develop into mature functioning blood cells.

Blood Corpuscular Elements Ppt Download
Definition Of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Nci Dictionary Of Cancer Terms National Cancer Institute

A Mature Erythrocytes And One Immature Erythrocyte Of T Tropicanus Download Scientific Diagram
No comments for "Which Term Describes Immature Red Blood Cells"
Post a Comment